DomainTools Investigations has uncovered a rapidly growing malware network aimed at Chinese-speaking users around the world.
The operation began in June 2023 and has now expanded to nearly 5,000 domains. More than 1,900 of those appeared between May and November 2025, showing how fast the campaign is scaling.
This study also highlights a key win for defenders: agentic AI systems processed the investigation 10x faster than traditional manual analysis.
The threat actor running this “super cluster” has clearly adapted over time. Earlier attacks depended on Alibaba Cloud Hong Kong, but recent activity shows a shift to a more scattered setup.
Since August 2025, the group has been registering domains through Chinese providers and using random domain names to hide their activity.
Even with these changes, analysts can still link the campaigns together. Repeated SOA emails, reused SEO tracking codes, and recognizable registrant details connect the 1,900 new domains back to the larger operation.
Today, the malware network stretches across five countries and uses eight registrars, up from only three at the start of 2025.
AI Agents Boost Malware Investigation Speed
Researchers turned to a next-generation AI system to manage the overwhelming number of malicious domains in this campaign.
The system works by breaking tasks into small pieces and assigning them to different AI agents, while a main controller oversees the workflow.
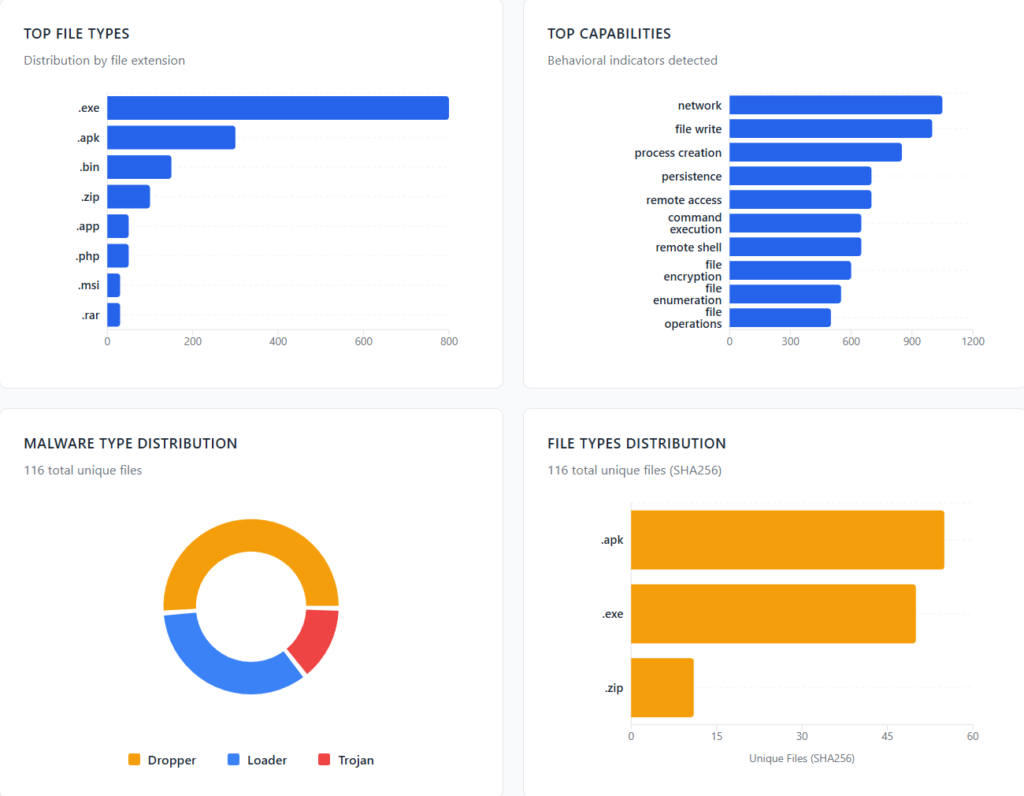
With this setup, the team was able to review more than 1,900 malware sites — a workload that would normally take manual analysts far longer, often limited to only a few hundred in the same time.
In testing, three AI agents analyzed 2,000 domains in about 10 hours, taking 1–10 minutes per site. They were able to fully examine pages packed with anti-bot scripts that normally block standard scanners. Unlike fixed automation, the agentic system adapts its approach as it investigates.
The AI agents were able to spot malicious code, pull down payloads, and even create YARA rules on their own — a shift that makes defending against large campaigns far more efficient.
Focused Spoofing Attacks on Chinese-Speaking Users
This cluster is heavily targeting Chinese-speaking users by creating fake versions of popular apps. These spoofed apps are used to install trojans and steal credentials.
From the 2,393 newest domains, most are impersonating communication tools and VPN apps — especially services people use to bypass internet restrictions. The attackers also use very large files (100–250MB) so basic antivirus scanners skip them.
Top Spoofed Application Categories (May–Nov 2025)
| Category | Domain Count | Share | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Communication Tools | 391 | 24.2% | WhatsApp, WhatsApp Web |
| VPN Services | 363 | 22.4% | LetsVPN (Kuailian), variants |
| Productivity | 229 | 14.2% | Google Services, Youdao, WPS Office |
| Web Browsers | 109 | 6.7% | Google Chrome |
| Crypto & Finance | 105 | 6.5% | ImToken, AICoin |
The group’s continued growth, shift to domestic registrars, and improved hiding techniques suggest it may be evolving into a service model where multiple affiliates can distribute their own malware.
But the use of agentic AI gives defenders a strong advantage — it finally allows analysis at the same scale as these massive threat networks.













Leave A Comment