
Google has uncovered a new form of AI-assisted malware that uses its own Gemini large language model (LLM) to rewrite its code and evade detection.
The malicious script, called PROMPTFLUX, was discovered by the Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG).
AI-Driven Malware Built in VBScript
According to Google, PROMPTFLUX is written in Visual Basic Script (VBScript) and communicates directly with Gemini’s API to request custom obfuscation and evasion techniques.
This process allows the malware to modify its own source code in real time — a behavior Google describes as “just-in-time self-modification.”
The malware includes a module called “Thinking Robot,” which regularly queries Gemini 1.5 Flash or later to generate new versions of its code.
It uses a hard-coded API key to interact with the Gemini API endpoint and stores the modified files in the Windows Startup folder to maintain persistence.
In addition, PROMPTFLUX attempts to spread through removable drives and network shares, potentially expanding its reach within target environments.
Experimental but Evolving Threat
GTIG noted that PROMPTFLUX appears to be in the testing phase.
While it currently lacks the ability to fully compromise systems, it shows the intent of creating metamorphic malware capable of evolving continuously.
Log files named “thinking_robot_log.txt” found on infected systems support this theory.
A newer version of PROMPTFLUX even prompts Gemini to rewrite its full source code every hour, effectively functioning as a self-regenerating malware prototype.
Expert Reactions: Hype or Reality?
Not everyone agrees with the severity of the findings.
Security researcher Marcus Hutchins commented on LinkedIn that the threat may be “overblown.”
He argued that the malware’s assumption that Gemini “instinctively knows how to evade antiviruses” is unrealistic.
Hutchins also noted that the self-modifying function was commented out and the script lacked proper entropy to ensure that each regenerated version differs from the previous one.
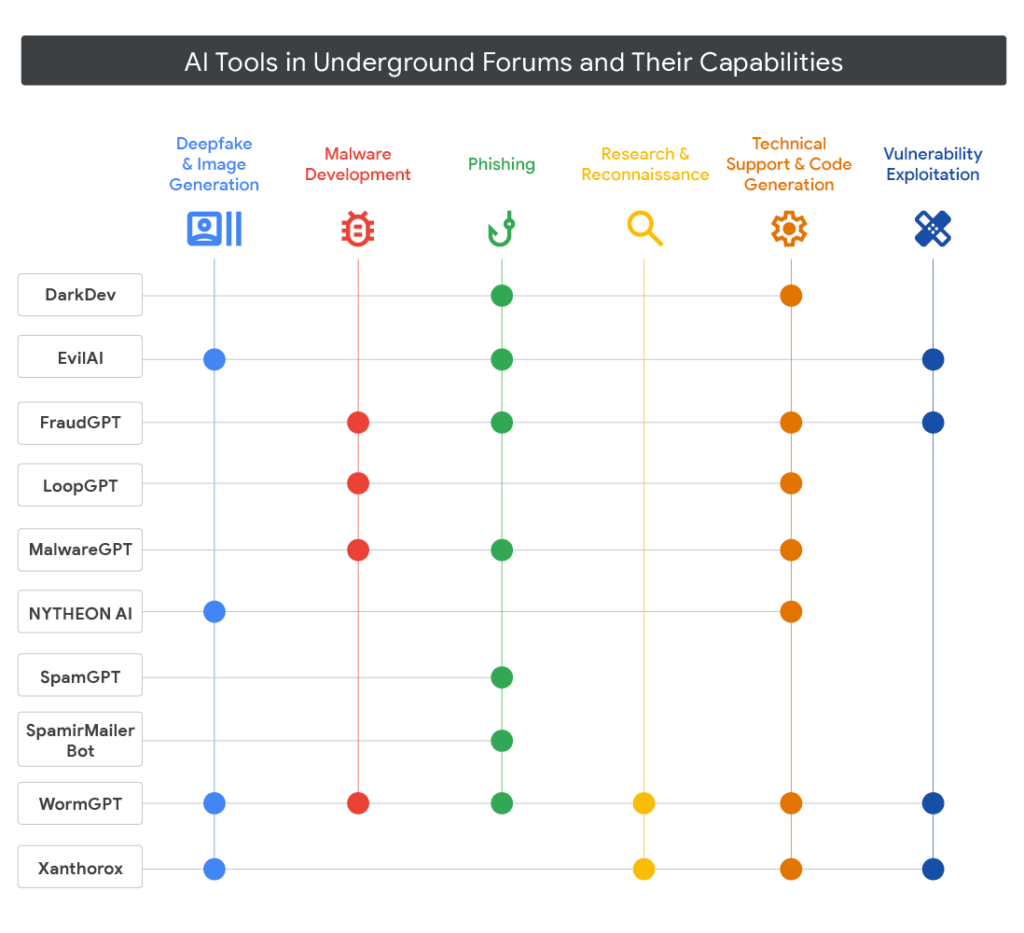
AI Abuse Extends Beyond PROMPTFLUX
Google’s research revealed that PROMPTFLUX is not the only LLM-assisted malware observed in the wild.
Other AI-driven threats include:
- FRUITSHELL: A PowerShell reverse shell that uses prompts to bypass detection.
- PROMPTLOCK: Cross-platform ransomware written in Go, which generates malicious Lua scripts at runtime.
- PROMPTSTEAL (LAMEHUG): A data-stealing tool linked to Russian APT28, which uses Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct for command generation.
- QUIETVAULT: A JavaScript-based credential stealer targeting GitHub and NPM tokens.
Gemini Misuse by State-Sponsored Actors
Google also found that nation-state threat groups from China, Iran, and North Korea are abusing Gemini to enhance their hacking operations.
Examples include:
- China-nexus actors using Gemini for reconnaissance, phishing, and data exfiltration.
- Iran’s APT41 using it for code obfuscation and C2 development.
- MuddyWater using AI to research custom malware while pretending to be students or researchers.
- APT42 creating phishing materials and translating lures for espionage.
- North Korea’s UNC1069 and TraderTraitor leveraging Gemini to develop code for cryptocurrency theft and fake software update scams.
Some Chinese actors reportedly posed as Capture-the-Flag (CTF) participants to trick Gemini into generating exploit code by claiming their queries were for “training exercises.”
Deepfakes and Expanding Threat Landscape
In a related finding, GTIG observed UNC1069 using deepfake videos and images of cryptocurrency professionals to distribute a backdoor called BIGMACHO, disguised as a legitimate Zoom SDK.
This campaign mirrors tactics seen in Kaspersky’s GhostCall report earlier this year.
Google Warns of Growing AI Weaponization
Google warned that AI-assisted cyberattacks are becoming the norm.
As more organizations integrate AI into daily workflows, attackers are learning to exploit these same systems for malicious purposes.
“Threat actors are rapidly refining their techniques,” GTIG said. “The low-cost, high-reward nature of AI-based attacks makes them an attractive option.”




