A widespread web server misconfiguration issue has quietly exposed millions of websites to potential data theft and unauthorized system access, according to new research from the Mysterium VPN research team.
The 2026 study found that nearly five million web servers worldwide are publicly exposing their hidden .git repositories — directories used by the Git version control system to track code history and development changes.
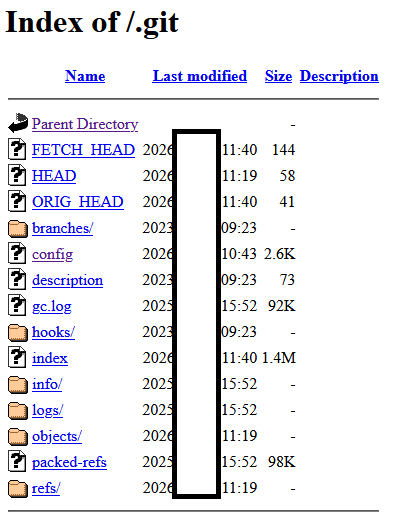
These repositories are intended to remain on developer systems or private infrastructure. When they appear on live production servers, they become a serious security liability.
The Scale of Exposure
Internet-wide scanning identified 4,964,815 IP addresses with accessible .git metadata. Of those, 252,733 systems exposed the .git/config file, which frequently contains deployment credentials such as API keys, usernames, and service passwords. This represents a credential exposure rate of just over five percent among vulnerable servers.
The geographic spread largely mirrors global cloud infrastructure distribution. The United States accounted for the largest share of exposed systems, followed by Germany, France, India, Singapore, the Netherlands, Japan, Russia, the United Kingdom, and Hong Kong.
How the Exposure Happens
The root cause is typically operational oversight during deployment. Developers often copy entire project directories to production servers, unintentionally including the hidden .git folder.
Many web server configurations do not restrict access to dot-prefixed directories by default, allowing attackers to directly browse or download repository data via a web browser.
An exposed .git repository does more than reveal code — it exposes the full development history. Attackers can reconstruct previous versions, identify vulnerabilities, and analyze internal architecture decisions.
The security impact can include:
- Source code disclosure, enabling intellectual property theft
- Credential harvesting, particularly from .git/config files
- Infrastructure mapping, giving attackers insight into backend systems
- Supply chain compromise, where stolen credentials allow insertion of malicious code into repositories or deployment pipelines
Because this data originates from legitimate development workflows, it often bypasses traditional security monitoring.
Mitigation and Defensive Measures
Security specialists emphasize that this risk is preventable with proper deployment hygiene. Web administrators should enforce server rules that deny external access to .git directories and other hidden paths. Production build pipelines must be configured to exclude version control artifacts entirely.
Any organization discovering exposure should immediately assume credential compromise, revoke affected keys and passwords, and rotate secrets across connected services.
Follow Us on: Linkedin, Instagram, Facebook to get the latest security news!











Leave A Comment