The “ClickFix” tactic exploits fake Google Meet and Zoom pages to deliver advanced malware, mimicking legitimate video conferencing platforms used for business and personal communication.
The Sekoia TDR team monitors this evolving social engineering method, which displays deceptive error messages in browsers to prompt users into running malicious PowerShell commands, ultimately infecting their systems.
How ClickFix Operates
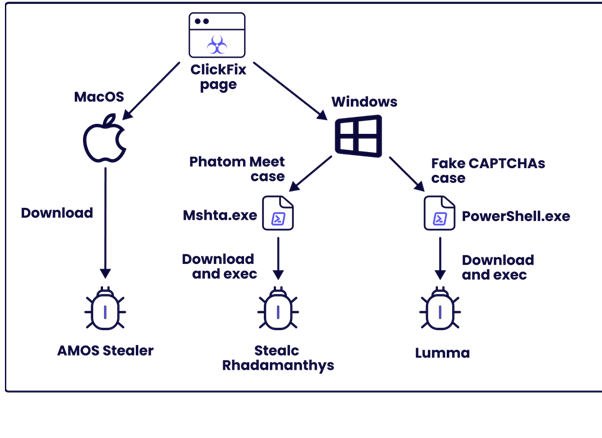
The ClickFix infection process is alarmingly simple and relies on user interaction to succeed.
- Error Message Display: When users visit the counterfeit video conferencing pages, they are presented with a fake error message claiming there’s a problem with their microphone or headset. This message is designed to create a sense of urgency and confusion, prompting users to take immediate action.
- User Action Required: To address the supposed issue, users are guided to press “Windows + R” to open the Run dialog box. This step appears harmless but is crucial for the subsequent malicious action.
- Malicious Command Execution: Users are then instructed to copy a malicious command displayed on the page and paste it into the Run dialog box. This command typically involves PowerShell scripts designed to execute harmful actions on the user’s system, allowing the malware to infiltrate and compromise their device.
This method effectively leverages social engineering tactics to manipulate users into unwittingly executing malware, highlighting the dangers of seemingly innocuous interactions on the web.
ClickFix can operate in several scenarios:
- macOS Target: Users are tricked into downloading a .dmg file that directly executes the malware.
- Windows Target: Two main infection chains are used: one with a malicious Mshta command and the other with PowerShell.
Each scenario exploits user trust in familiar interfaces like Google Meet to deliver malware.
Detecting ClickFix requires vigilance and awareness of key indicators:
- Process Monitoring: Watch for unusual parent-child relationships, such as mshta.exe or bitsadmin.exe launched by Explorer.exe.
- Network Activity: Monitor suspicious network requests from processes like mshta.exe using typical Internet Explorer User-Agent strings.
Organizations should employ EDR systems to identify these patterns and analyze firewall and proxy logs for potential compromises.
ClickFix exploits legitimate Windows tools, known as “living off the land,” to bypass security measures. This emphasizes the need for strong monitoring systems. As attackers target trusted platforms like Google Meet and Zoom, vigilance is crucial. Understanding these tactics and implementing detection strategies can help mitigate risks from ClickFix and similar threats.
Follow Us on: Twitter, Instagram, Facebook to get the latest security news!











Leave A Comment