
MacOS users are seeing a sharp rise in password-stealing malware, spread through fake apps and ads. Leading threats include “Atomic Stealer,” “Poseidon Stealer,” and “Cthulhu Stealer,” each using unique tactics, according to Palo Alto Networks’ Unit42.
MacOS password-stealing malware
Atomic Stealer (AMOS) was first found in April 2023 and is sold as malware-as-a-service (MaaS) on hacker forums and Telegram. It has evolved from Go to C++, with some versions using Python scripts or Mach-O binaries. Spread through malvertising, it steals browser passwords, cryptocurrency wallets, and instant messaging data.
Execution Flow: Atomic Stealer pretends to be a legitimate installer and tries to access files like /Users/$USER/Library/Application Support/Google/Chrome/Default/Login Data to steal Chrome login credentials.
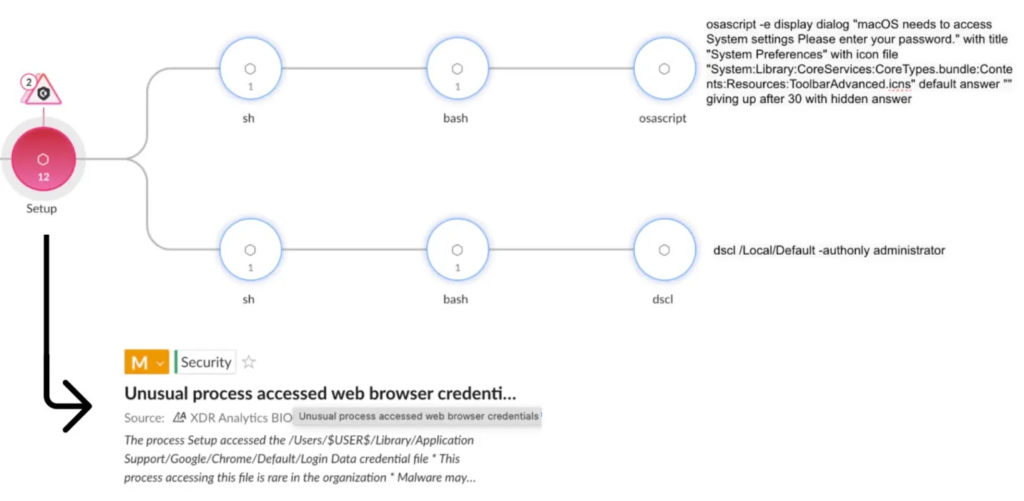
Poseidon Stealer: Created by “Rodrigo4,” supposedly a former Atomic Stealer developer, Poseidon Stealer spreads through fake installers, Google ads, and malicious emails. It uses an encoded AppleScript to run its main logic and tricks users into entering their passwords during installation.
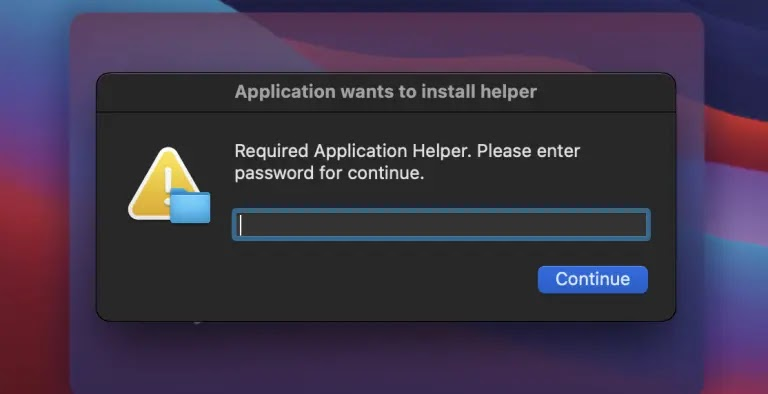
How It Works:
Once installed, Poseidon Stealer prompts users for their password and steals browser passwords, cryptocurrency wallets, macOS Notes, and Telegram data, sending them to attacker-controlled servers.
Cthulhu Stealer: Sold on Telegram by the “Cthulhu Team,” this malware is written in Go and spread through fake app installers. It steals browser credentials, cryptocurrency wallets, and files like .png, .jpg, and .pdf.

How It Works:
Cthulhu Stealer tricks users with fake password prompts, including MetaMask requests. It saves stolen data in /Users/Shared/NW and uploads it to a command-and-control server.
Recommendation:
To protect against these threats, organizations should deploy advanced detection tools like Cortex XDR, which can analyze credential theft and sensitive data exfiltration. These tools help monitor suspicious AppleScript executions and unauthorized file access.
Additionally, adopting multi-layered defense strategies and staying updated on emerging threats are essential for protecting sensitive information.
Indicators of Compromise (IoC):
- SHA256 Hashes for Atomic Stealer:
- 599e6358503a0569d998f09ccfbdeaa629d8910f410e26df0ffbd68112e77b05
- a33705df80d2a7c2deeb192c3de9e7f06c7bfd14b84f782cf86099c52a8b0178
- IP Addresses for Atomic Stealer C2 Servers:
- 94.142.138[.]177
- 194.169.175[.]117
- SHA256 Hashes for Poseidon Stealer:
- 9f4f286e5e40b252512540cc186727abfb0ad15a76f91855b1e72efb006b854c
- 5880430d86d092ac56bfa4aec7e245e3d9084e996165d64549ccb66b626d8c56
- IP Addresses for Poseidon Stealer C2 Servers:
- 194.59.183[.]241
- 70.34.213[.]27
Follow Us on: Twitter, Instagram, Facebook to get the latest security news!




