
Cofense Intelligence researchers have uncovered a phishing method that uses Blob URIs to sneak fake login pages into users’ inboxes while avoiding email security filters.
Blob URIs, normally used by browsers to handle things like images or video, are now being misused by attackers to hide malicious content in emails.
Even trusted sites like YouTube use Blob URIs for safe data storage, but cybercriminals are now using the same feature to make phishing pages look real and bypass security checks.
Phishing Attack Uses Browser Trick to Bypass Email Security
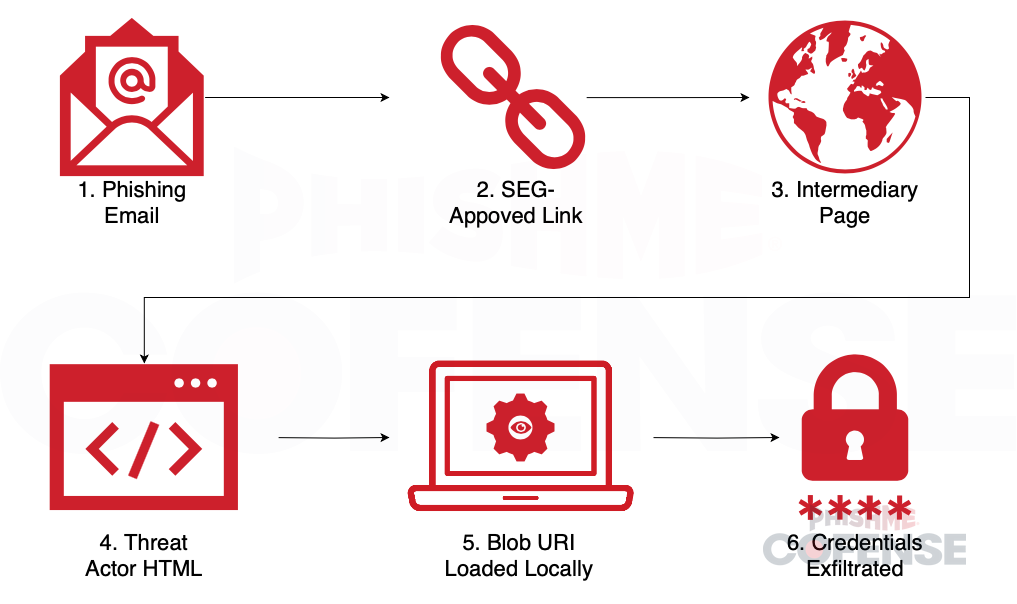
The attack starts with a phishing email that avoids detection by using safe-looking topics like encrypted messages or financial alerts.
Instead of linking directly to a fake site, the email sends users to a trusted domain like onedrive.live.com. This helps it pass email filters.
From there, users are redirected to a hacker-controlled page that loads a fake login form into the browser using a Blob URI—local data that can’t be scanned by security tools.
These phishing pages look like real services, such as OneDrive, and steal login credentials once the user submits them.
How Blob URIs Help Hackers Stay Hidden
Cofense reports that Blob URIs make phishing attacks harder to detect because they are created inside the victim’s browser and can’t be scanned by most security tools.
Attackers also use trusted websites, like Microsoft services, to redirect users. This makes the emails seem safe and reduces suspicion.
Once users land on the trusted page, they’re quietly redirected to a fake login screen stored as a Blob URI, making it easier to steal their credentials without raising alarms.
Blob URI-based phishing uses clever redirects and obscure browser functions to bypass email security and trick users. Because the content only loads inside the victim’s browser, AI and automated tools often miss it.
This technique is gaining traction as it avoids traditional detection methods, making it harder for defenders to respond.
To counter it, organizations need to focus on user training and behavioral threat detection, since standard tools can’t see what’s happening inside the browser.




