Attackers used the EternalBlue vulnerability to access the observatory farm, create a hidden admin share, and run a malicious batch file named p.bat, which opened firewall ports, set up port forwarding, and scheduled tasks for persistence.
It included anti-detection mechanisms to obstruct analysis, and a malicious executable disguised as svchost.exe was created to disable Windows Defender and set exclusions to avoid detection.
It also carried out actions like opening firewall ports, configuring port forwarding, and scheduling tasks.The attackers deleted the administrative share to conceal their presence and retain control of the system.
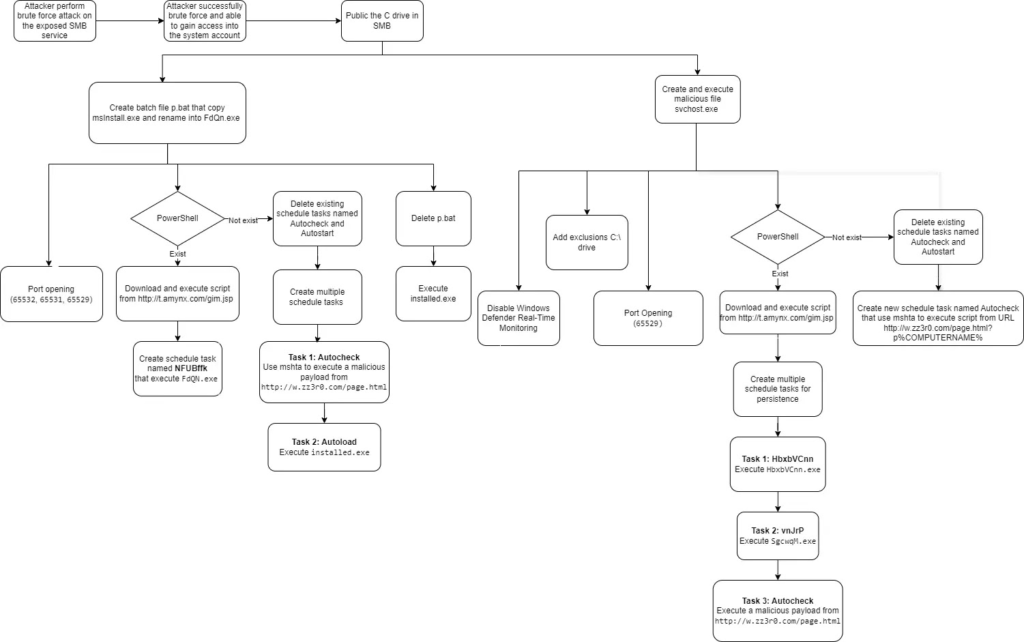
The attacker brute-forced SMB to access the local administrator account and created a hidden administrative share on the C: drive for persistence.
A malicious batch script (p.bat) configured firewall rules, disguising outbound traffic as DNS traffic via port 53 to a remote server (1.1.1.1). Scheduled tasks were also set up to run the batch script and potentially download malware (installed.exe) regularly.
The script checks for PowerShell, and if found, it downloads and runs another script from a malicious LemonDuck URL. It also creates a task to run FdQN.exe every hour. If PowerShell isn’t available, it uses Windows Scheduler to run malicious scripts (mshta and installed.exe) at set intervals.
It tries to start a service (Ddriver) and monitors command prompts. If it detects over 10, it reboots the system, then deletes itself and p.bat before running another malware (installed.exe).
The malware disables Windows Defender’s real-time monitoring, excludes the C drive from scans, and opens a port for potential C2 communication.
To avoid detection, it renames malicious executables and downloads additional scripts via PowerShell or scheduled tasks. If PowerShell is unavailable, it restarts the Task Scheduler service and replaces tasks to fetch a malicious payload every 50 minutes, indicating it uses multiple download URLs and task names for persistence.
NetbyteSec’s analysis identified msInstall.exe, a LemonDuck variant, as a malicious executable targeting remote systems. It uses brute-force attacks with user/password lists to gain access and exploits the EternalBlue vulnerability (CVE-2017-0144) for SYSTEM privileges.
The malware establishes persistence by copying itself, creating scheduled tasks, and possibly modifying firewall rules. It also attempts to download more malicious scripts and uses Mimikatz to steal credentials, allowing lateral movement within the network.
Follow Us on: Twitter, Instagram, Facebook to get the latest security news!
Follow Us on: Twitter, Instagram, Facebook to get the latest security news!