ESET researchers recently identified new Android malware called “Ngate” that allows hackers to withdraw money from victims’ payment cards.
Ngate malware
NGate Android malware, identified in November 2023, represents a sophisticated method for unauthorized ATM withdrawals. It exploits a modified version of the NFCGate tool, originally developed for NFC research, to relay Near Field Communication (NFC) data from victims’ payment cards through compromised Android smartphones to attackers’ devices.

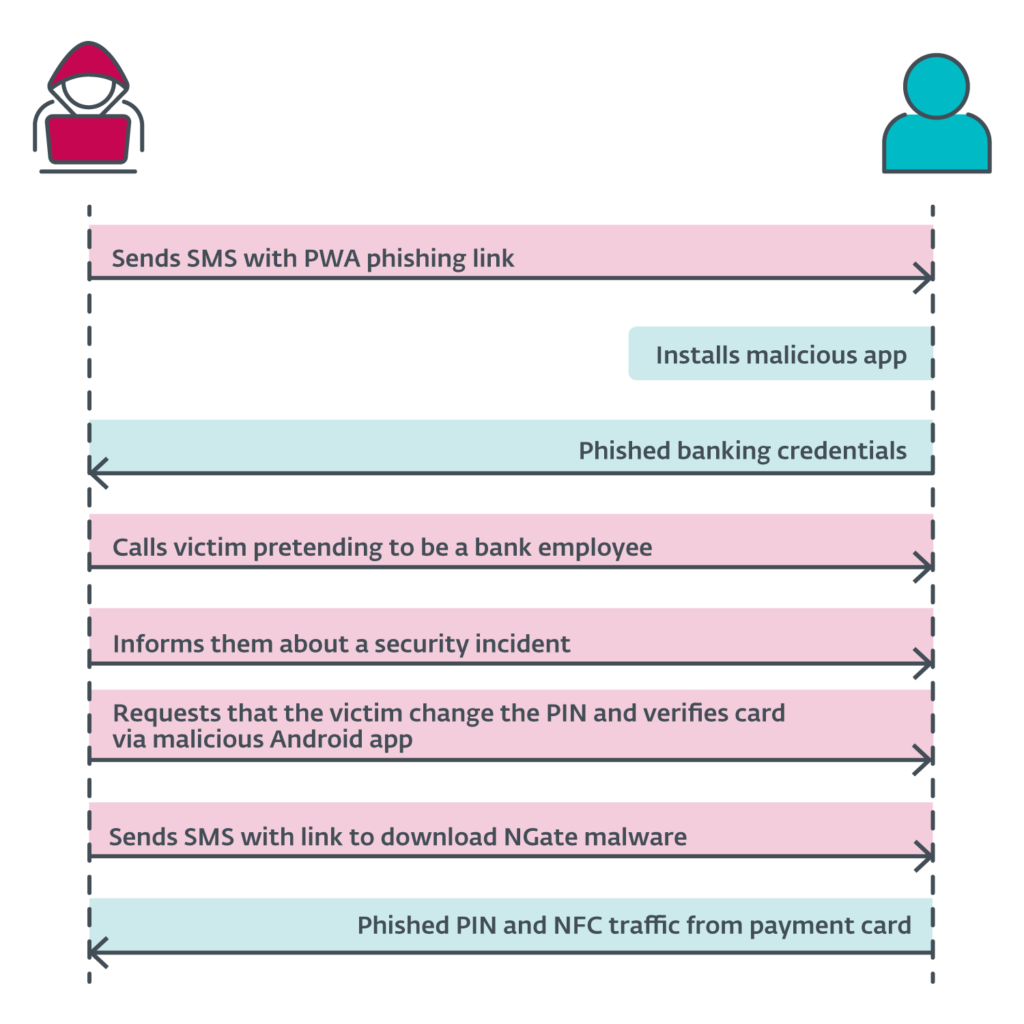
The malware was distributed via phishing websites that initially impersonated prominent Czech banks as Progressive Web Apps (PWAs). These sites later evolved into WebAPKs, which closely mimic native applications, making them more convincing and increasing the likelihood of successful infections.
The attack began with SMS phishing, tricking victims into visiting malicious sites disguised as tax return forms. Victims were then deceived by fake bank employee calls into installing NGate, thinking it would secure their compromised accounts.
Once installed, NGate captures banking credentials and asks victims to place their payment cards against their phones. This allows the malware to relay NFC data to attackers. The attack only requires the attacker’s device to be rooted, not the victim’s.
The malware had a backup method to transfer funds directly between accounts if the NFC relay failed. This campaign, targeting clients of three Czech banks, ran from November 2023 to March 2024 and was disrupted by the arrest of a 22-year-old suspect in Prague.
NGate stands out for misusing legitimate NFC research tools for crime, potentially enabling future attacks like NFC tag cloning and payment card emulation.
The total financial damage is unclear, but Czech police recovered over €6,000 from the last three victims at the time of the arrest. The malware, identified by the package name rb.system.com, used WebViews to display phishing sites mimicking banks like Raiffeisenbank and ČSOB.
NGate used JavaScript to control devices and initiate NFC relay attacks via two servers for phishing and NFC traffic redirection. The malware evolved from PWA/WebAPK attacks to NFC relaying, indicating increasing sophistication. The campaign is paused after an arrest but shows potential for future attacks.
Recommendation
- Educate Users: Teach people about phishing and not to install unknown apps.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update devices and apps.
- Use Security Software: Install and use good antivirus and anti-malware tools.
- Limit NFC Use: Restrict NFC features to trusted apps and devices.
- Download from Trusted Sources: Only get apps from official stores and verify them.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication: Add extra security for sensitive accounts.
- Conduct Security Audits: Regularly check for and fix security weaknesses.
IoCs
Files
| SHA-1 | Filename | Detection | Description |
| 7225ED2CBA9CB6C038D8 615A47423E45522A9AD1 | csob_smart_klic.apk | Android/Spy.NGate.B | NGate Android malware. |
| 66DE1E0A2E9A421DD16B D54B371558C93E59874F | csob_smart_klic.apk | Android/Spy.NGate.C | NGate Android malware. |
| DA84BC78FF2117DDBFDC BA4E5C4E3666EEA2013E | george_klic.apk | Android/Spy.NGate.C | NGate Android malware. |
| E7AE59CD44204461EDBD DF292D36EEED38C83696 | george_klic-0304.apk | Android/Spy.NGate.C | NGate Android malware. |
| 103D78A180EB973B9FFC 289E9C53425D29A77229 | rb_klic.apk | Android/Spy.NGate.A | NGate Android malware. |
| 11BE9715BE9B41B1C852 7C9256F0010E26534FDB | rb_klic.apk | Android/Spy.NGate.C | NGate Android malware. |
Network
| IP | Domain | Hosting provider | First seen | Details |
| 91.222.136[.]153 | raiffeisen-cz[.]eu | Hosting Ukraine LTD | 2024‑03‑05 | NGate distribution website. |
| 104.21.7[.]213 | client.nfcpay.workers[.]dev | Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑03‑03 | Phishing website. |
| 172.187.98[.]211 | N/A | Divya Quamara | 2024‑04‑07 | NGate C&C server. |
| 185.104.45[.]51 | app.mobil-csob-cz[.]eu | Hosting Ukraine LTD | 2024‑03‑12 | NGate distribution website. |
| 185.181.165[.]124 | nfc.cryptomaker[.]info | Serverius | 2024‑02‑21 | NGate C&C s |
Follow Us on: Twitter, Instagram, Facebook to get the latest security news!