A phishing scam through Google search left thousands of stolen passwords exposed.
Phishing Campaign
A phishing campaign exposed thousands of corporate employees credentials.
In august, attackers initiated a phishing campaign prompting users to open a malicious HTML attachment.
Follow Us on: Twitter, Instagram, Facebook to get the latest security news!
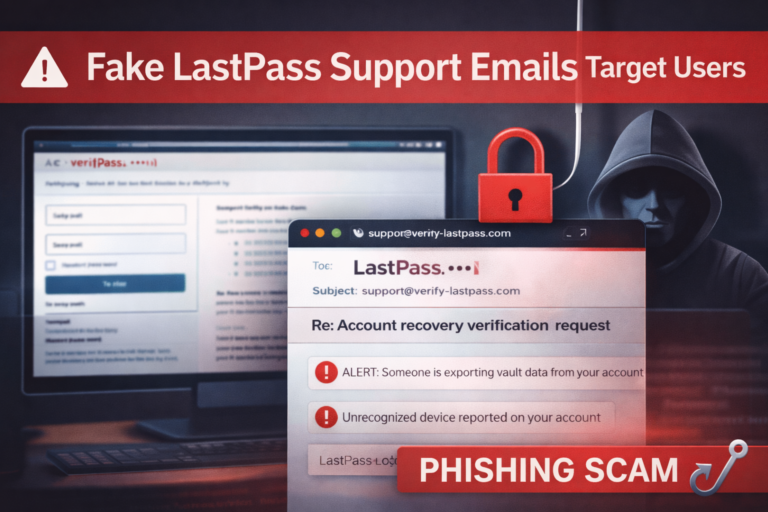
According to Check Point Research, users receive phishing mail with first name or company title in the subject line.

Once double-clicked the attached HTML file, when opened, urges recipients to enter their Office 365 passwords on a fake lookalike login page.
And, at once the attachment opened,
- the embedded JavaScript code runs in the background, which has a function: covert background checks of password use
- the entered passwords which were then extracted and sent to a remote server in a text file
- once, the credentials were given, they would be harvested and users redirected to legitimate login pages
The attackers use web of websites, each domain used as “drop-zone servers” for processing incoming, stolen credentials.
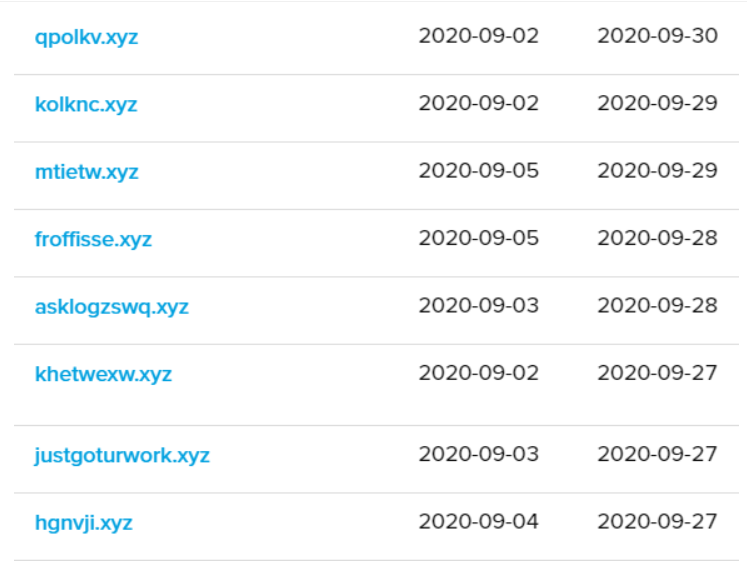
However, the server would run for roughly two months with dozens of XYZ domains, that were used for phishing attacks.
Importantly, attackers evade from Anti-Virus software’s using simple techniques.
The Check Point team noted “Attackers usually prefer to use compromised servers instead of their own infrastructure because of the existing websites’ well-known reputations,”.
Also, “The more widely recognized a reputation is, the chances are higher that the email will not be blocked by security vendors.”
Researchers came to conclusion while analyzing the different email headers used in this campaign,
- The emails — sent from a Linux server hosted on Microsoft’s Azure
- The emails — often sent by using PHP Mailer 6.1.5 (latest version from Mar 19 to May 27)
- And, The emails — delivered using 1&1 email servers
Security Recommendations:
On the other hand, Check Point reached out to Google and informed them of the credential indexing.
Comparing the campaign happened on August 2020, used the same JavaScript encoding, which shows — this operation is active for long time.
Practical tips Check Point suggests that help to keep your data safe:
- Beware of lookalike domains, spelling errors in emails or websites, and unfamiliar email senders.
- Be cautious with files in email from unknown senders
- Ensure you are ordering goods from an authentic source. One way to do this is to NOT click on promotional links in emails, and instead, Google your desired retailer and click the link from the Google results page.
- Beware of “special” offers that don’t appear to be reliable or trustworthy purchase opportunities.
- Make sure you do not reuse passwords between different applications and accounts.