Cybercriminals are exploiting Binance smart contracts as intermediary C2 servers, favoring them due to their resilience against takedowns. Initially used for deploying infostealers, these smart contracts have potential applications for distributing various types of malware.
A new technique, EtherHiding, was described over half a year ago, in October 2023. Analysts observed a shift in the networking patterns of an older scheme that deceives users into installing malware disguised as browser updates. Instead of fetching malicious code from Cloudflare Workers, attackers now direct their requests towards smart contracts on Binance.
Smart contracts, essentially code executed when specific conditions are met, operate similarly to Cloudflare Workers, which previously allowed fraudsters to use legitimate Cloudflare servers for hosting malicious code. The difference lies in smart contracts being hosted on a blockchain, making them nearly impossible to take down. This resilience likely contributes to cybercriminals’ increased interest, besides their cost-effectiveness.
HOW MALWARE UTILIZES BINANCE SMART CONTRACTS
The attack chain starts with compromising a website, often targeting WordPress sites due to numerous vulnerabilities in both the WordPress core and popular plugins. Once compromised, hackers install a specific script that communicates with the Binance web API.
During these operations, attackers create a new smart contract and inject the malicious code using the contract’s update function, setting the scheme to a “ready-to-fire” state.
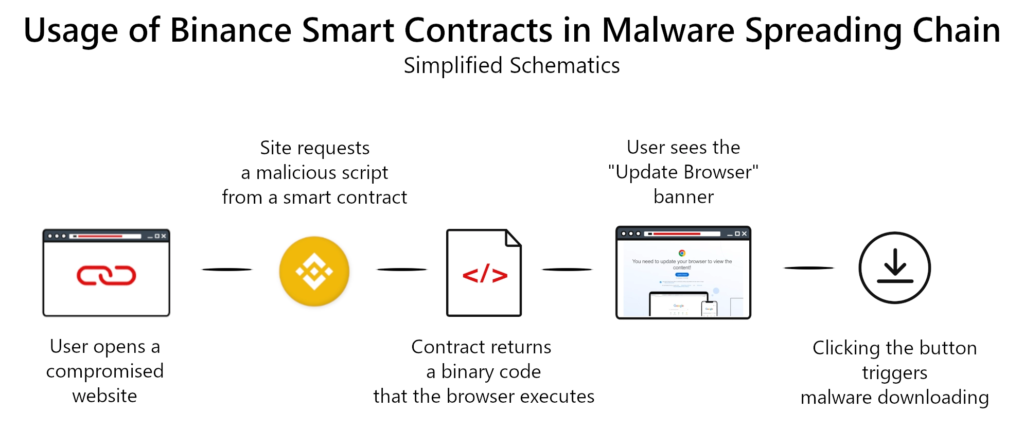
Users accessing compromised sites trigger a mechanism that sends a get() request to a linked smart contract. The response, containing a binary code string, executes in the browser via eval(), defacing the site and displaying a deceptive “update browser” banner.
Clicking this prompts the execution of a script from the smart contract, downloading the final payload, often used by malware like Lumma Stealer, Redline, and Vidar.
Estimating the risks posed by this method is challenging, but it offers several significant advantages over previous adversary tactics.
Foremost, Binance Smart Contracts are nearly impervious to takedowns, a characteristic highly valued by cybercriminals who are willing to invest in “bulletproof” hosting services. These hosts operate with minimal downtime and avoid cooperation with law enforcement, making them ideal for malicious infrastructure.
Binance Smart Contracts also benefit from blockchain technology within a major cryptocurrency exchange, providing robust resilience against DDoS attacks and maintaining anonymity.
Operating smart contracts requires no personal data and stores no information about their creator, further enhancing their appeal for illicit activities.
Exploiting Binance Smart Contracts offers cost-effectiveness, with minimal fees for creation and updates ($0.2 – $0.6), allowing frequent modifications. This method could dramatically change malware distribution, surpassing traditional bulletproof hosting in terms of affordability and effectiveness.
Defending Against Malicious Binance Smart Contracts
While disrupting the scheme involving malicious Binance contracts may seem challenging, the attack comprises multiple steps where effective anti-malware software can intercept and halt the malware.
Follow Us on: Twitter, Instagram, Facebook to get the latest security news!













Leave A Comment