The pandemic has spurred significant shifts in business models. With the rise of digital transformation, increased efficiency, and profitability, the threat landscape for organizations has evolved. Presently, with over 60% of businesses globally adopting remote or hybrid work models, reliance on digital channels, especially corporate email addresses, has become paramount for most internal and external communications.
What is Business Email Compromise (BEC)
Business Email Compromise (BEC) is a type of cybercrime where attackers gain unauthorized access to a business email account and then use it to deceive employees, customers, or partners into taking actions that benefit the attacker. This typically involves tricking individuals into transferring funds, providing sensitive information, or performing other actions that can result in financial loss or data compromise.
BEC attacks often involve social engineering tactics, such as impersonating company executives, suppliers, or trusted partners. Attackers may use various techniques, including phishing emails, spoofed email addresses, and domain spoofing, to make their emails appear legitimate.
BEC attacks can have serious consequences for organizations, including financial loss, damage to reputation, and legal implications. It is important for businesses to implement robust security measures, such as email authentication protocols, employee training, and multi-factor authentication, to help prevent BEC attacks and mitigate their impact if they occur.
BEC attacks can extend to the relationships between organizations and their vendors within the supply chain. Attackers may impersonate a participant in the supply chain via email, urging modifications to invoice details within your company’s finance department and substituting them with the attacker’s account information.
Additionally, they might request fund transfers to accounts under their control using falsified invoices. Furthermore, as detailed further below, BEC attacks may result in the introduction of malicious software into your organization’s information system through email attachments.
A concerning instance illustrating the versatility of BEC attacks is the case of Puerto Rico’s government, which incurred millions of dollars in financial losses. An attacker gained control over an email address linked to the Puerto Rico Retirement System, prompting several victims, including the Puerto Rico Department of Industry and Development and Puerto Rico Tourism Companies, to make multimillion-dollar transfers. Many institutions were ensnared by emails purportedly from the Puerto Rico Retirement System, urging changes to account numbers for upcoming premium payments.
Rising Trend
Based on the FBI’s annual cybercrime reports, Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks saw 20,373 complaints in 2018, rising to 23,775 in 2019, then declining to 19,369 in 2020, and subsequently increasing to 21,832 in 2022. These figures reveal a 7.2% increase in BEC attacks over the last four years.
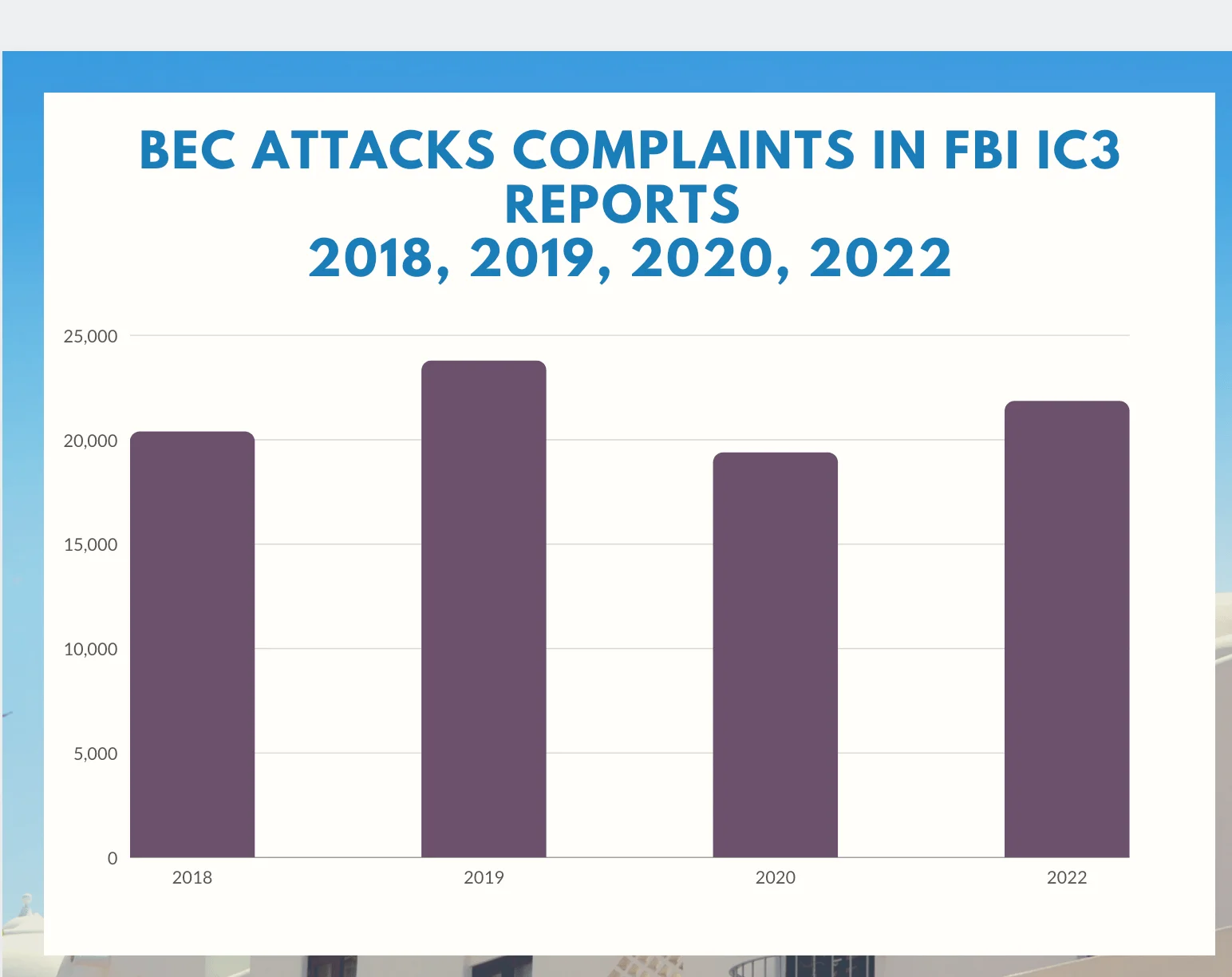
Although reported BEC attack cases have not experienced a dramatic surge, attackers’ techniques have grown more sophisticated, and the demanded amounts have notably escalated in tandem with the post-pandemic digitalization and adoption of remote work models. Losses stemming from BEC attacks climbed from $1.2 billion in 2018 to $1.7 billion in 2019, $1.8 billion in 2020, and $2.7 billion in 2022. These statistics indicate a 125% increase in BEC attacks over the past four years.
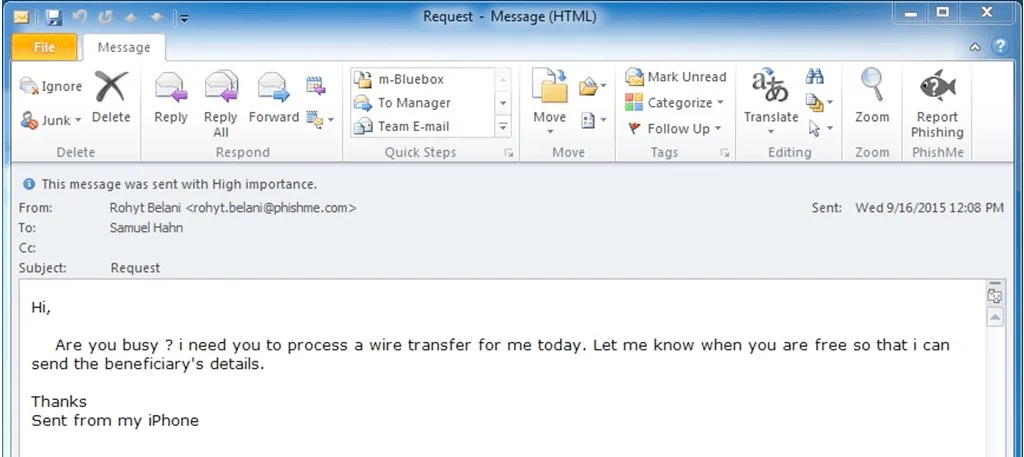
While numerous sophisticated security solutions concentrate on scrutinizing email attachments and identifying malicious file extensions, company employees remain susceptible to plain text emails composed in straightforward language.
As per the 2023 Email Security Report by Abnormal Security, over 98% of employees neglect to report BEC email attacks. Furthermore, the study highlights that entry-level employees react to text-based BEC emails in 78% of reported incidents, with sales and marketing departments particularly vulnerable.
Another significant revelation from Verizon’s 2023 DBIR report is that Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks are prominent in over 67% of all cases where data breaches occur following an initial compromise.
Preventing Business Email Compromise (BEC) Attacks
To prevent Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks, follow these key steps:
- Employee Training: Educate employees about the tactics used in BEC attacks, such as email spoofing, phishing, and social engineering. Provide regular training sessions to enhance awareness and vigilance among staff members.
- Email Authentication: Implement email authentication protocols such as SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to verify the authenticity of incoming emails and detect spoofed messages.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enable MFA for email accounts and other sensitive systems to add an extra layer of security, making it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Strong Passwords: Encourage employees to use strong, unique passwords for their email accounts and regularly update them to reduce the risk of account compromise.
- Verification Procedures: Establish verification procedures for financial transactions and sensitive requests, such as requiring dual authorization or confirmation through a separate communication channel.
- Vendor Management: Vet and monitor third-party vendors and suppliers, especially those with access to sensitive information or involved in financial transactions, to mitigate the risk of BEC attacks targeting supply chain relationships.
- Security Software: Deploy advanced email security solutions, including spam filters, anti-phishing tools, and endpoint protection, to detect and block malicious emails before they reach users’ inboxes.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly update an incident response plan to quickly identify and mitigate BEC attacks if they occur. This plan should include procedures for reporting incidents, isolating affected systems, and communicating with stakeholders.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities in email systems and other critical infrastructure, allowing for timely remediation and strengthening of defenses against BEC attacks.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about the latest BEC attack trends, techniques, and security best practices through industry reports, threat intelligence feeds, and security awareness training programs to adapt and improve your defenses accordingly.
Follow Us on: Twitter, Instagram, Facebook to get the latest security news!













Leave A Comment