Cybersecurity researchers have taken the wraps off a earlier undocumented spyware focusing on the Apple macOS working technique.
The malware, codename CloudMensis by Slovakian cybersecurity company ESET, is said to exclusively use public cloud storage services such as pCloud, Yandex Disk and Dropbox to receive commands from attackers and exfiltrate files.
Know about CloudMensis
CloudMensis, written in Objective-C, was first discovered in April 2022 and is designed to target the silicon architectures of Intel and Apple.
The initial infection vector for the attacks and targets are still unknown. But its very limited distribution is an indication that the malware is being used as part of a highly targeted operation against entities of interest.
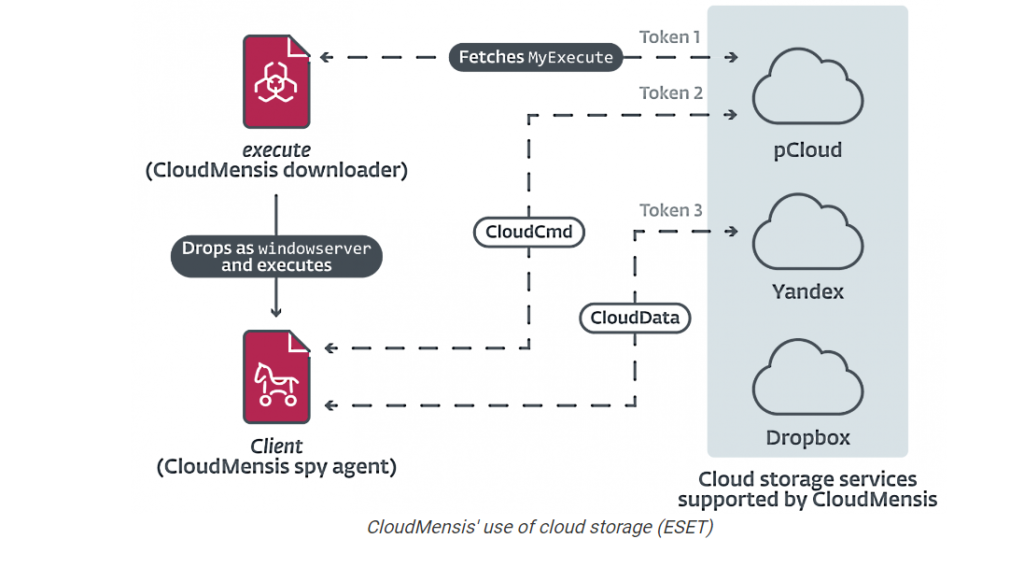
The attack chain noticed by ESET abuses code execution and administrative privileges to launch a 1st-phase payload which is utilized to fetch and execute . 2nd-stage malware hosted on pCloud, which, in turn, exfiltrates paperwork, screenshots, and email attachments, between some others.
The first-stage downloader is also known to erase traces of Safari sandbox privilege escalation and evasion exploits that use four security holes now fixed in 2017.
The implant also comes with features to bypass the Transparency, Consent and Control (TCC) security framework, which aims to ensure that all apps obtain user consent before accessing files.
On top of that, an analysis of metadata from the cloud storage infrastructure shows that the pCloud accounts were created on January 19, 2022, with the compromises commencing on February 4 and peaking in March.
However, “if SIP is enabled but the Mac is running any version of macOS Catalina earlier than 10.15.6, CloudMensis will exploit a vulnerability to make the TCC daemon (tccd) load a database CloudMensis can write to.”
Follow Us on: Twitter, Instagram, Facebook to get the latest security news!