Security researchers have discovered a sophisticated method, named “DHCP Coerce,” that exploits the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) administrators group to escalate privileges within Windows domains.
The vulnerability revolves around the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) service, crucial for network administration, as it automates IP address assignment, streamlining network connection management.
Yet, this convenience has a drawback. Attackers exploit the DHCP Administrators group through specific configurations and permissions, allowing them to escalate privileges within a Windows domain.
The exploitation process entails several technical steps, such as manipulating DHCP settings and deploying malicious scripts.
With elevated privileges, attackers can potentially seize control of the entire domain, accessing and manipulating data at their discretion.
This vulnerability is particularly alarming as it can be exploited remotely, without requiring physical access to the network.
This research reveals that even well-intentioned access controls can be manipulated maliciously. Exploiting DHCP settings and deploying malicious scripts, attackers gain elevated privileges to potentially seize control of the entire domain, accessing and manipulating data remotely.
The DHCP Administrators Group
The DHCP administrators group is an Active Directory (AD) group responsible for managing DHCP servers, with members typically granted limited permissions for querying and modifying DHCP service configurations.
Despite its intended limitations, the DHCP administrators group’s privileges can be exploited to execute code on DHCP servers, particularly concerning when the server is installed on a Domain Controller (DC).
Akamai researchers have identified a novel privilege escalation method targeting Active Directory (AD) environments, leveraging the DHCP administrators group to elevate privileges and gain unauthorized access to valuable resources.
DHCP Options
The DHCP options are configurations advertised to network clients, including IP addresses, subnet masks, and DNS server information. The researchers showed that attackers can manipulate these options to inject malicious configurations.
One such option is “Proxy autodiscovery,” which can be used to configure a web proxy and compromise client credentials.
The DHCP Coerce Technique
The DHCP Coerce technique manipulates the DNS Server option to redirect DHCP DNS Dynamic Updates to an attacker-controlled address, coercing the DHCP server to authenticate using Kerberos, which can then be relayed to compromise the server.
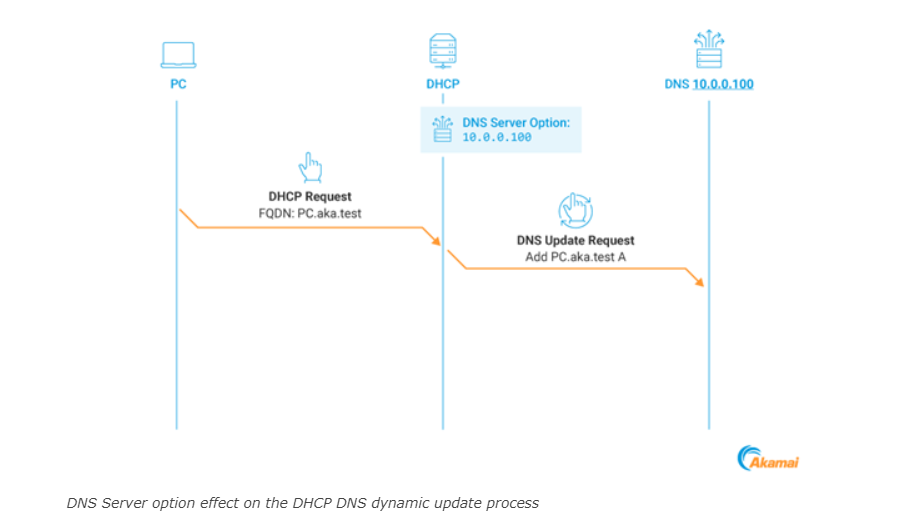
Kerberos Relay Attack
By coercing Kerberos authentication and relaying it, attackers can impersonate the DHCP server machine account, gaining full control over the server.
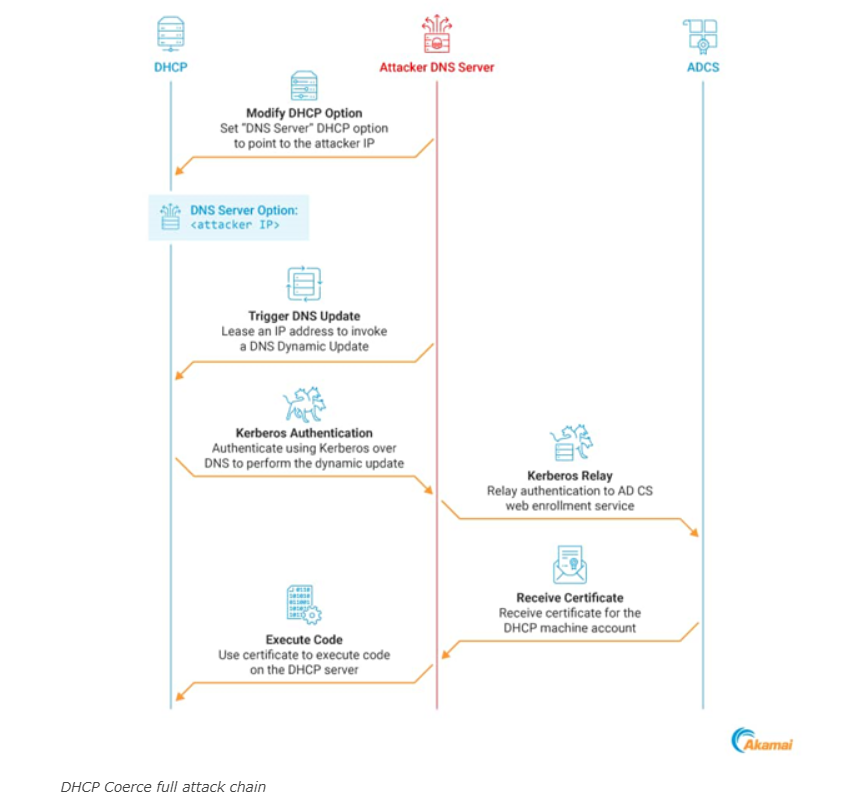
Mitigation
- DHCP Configuration Security
- Audit Logs: Monitor DHCP server logs for any unusual activities.
- Scope Limitation: Configure DHCP scopes carefully to limit unauthorized access.
- Snooping: Use DHCP snooping on switches to prevent fake DHCP messages.
- AD CS Relay Attack Mitigation
- LDAP Security: Enable LDAP signing and use LDAPS for secure communication.
- Authentication Protection: Implement Extended Protection for Authentication to prevent Man-in-the-Middle attacks.
- Kerberos Armoring: Deploy FAST to enhance Kerberos protocol security.
- DHCP Administrators Group Management
- Membership Audits: Regularly review DHCP administrators group membership for unauthorized users.
- Least Privilege: Limit group membership to essential personnel only.
- RBAC: Apply Role-based Access Control for precise access management.
- Network Segmentation
- VLANs: Implement VLANs for logical network segmentation.
- Firewall Rules: Enforce strict firewall rules between network segments to control traffic and prevent attacks.
- Data Separation: Store sensitive data in secure, segmented network zones.
- DNS Anomaly Detection
- Logging: Enable DNS query logging to detect unusual patterns.
- DNSSEC: Implement DNS Security Extensions for validating DNS response authenticity.
- Threat Intelligence: Utilize threat intelligence feeds to block known malicious domains and IPs.
Implementing these strategies can significantly enhance your network’s defense against DHCP abuse, AD CS relay attacks, and DNS anomalies. Regular updates and security protocol reviews are crucial for maintaining effective protection.
Follow Us on: Twitter, Instagram, Facebook to get the latest security news!













Leave A Comment