Two critical vulnerabilities in F5 Next-Gen Big IP have been uncovered, enabling threat actors to attain full administrative control of the device and establish accounts on any F5 assets. These attacker-created accounts remain invisible to the Next Central Manager, providing persistent access for various malicious activities.
CVE-2024-21793 and CVE-2024-26026 have been assigned to these vulnerabilities, both rated with a severity of 7.5 (High).
Furthermore, F5 has confirmed no signs of exploitation by threat actors in the wild. They have promptly released patches for these vulnerabilities along with security advisories.
F5 Next-Gen Manager Vulnerability
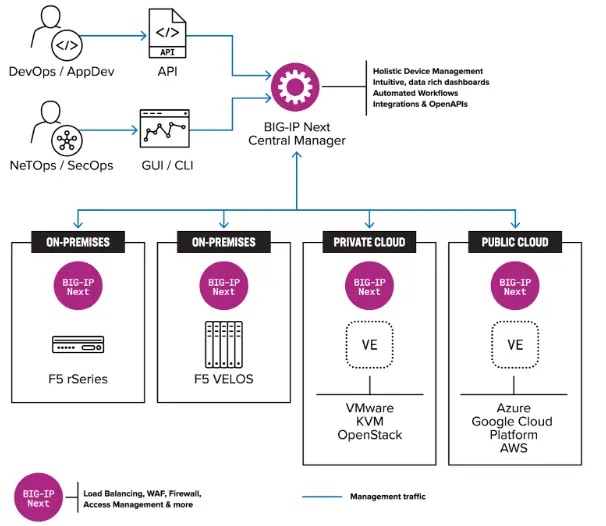
Threat actors have long targeted networking and application infrastructure due to their high privilege levels, providing avenues for access, spread, and persistence within environments. The Next Central Manager serves as a centralized control point for all life cycle-related tasks across BIG-IP.
CVE-2024-21793: Unauthenticated OData Injection
The vulnerability in the Central Manager stems from its handling of OData queries, potentially enabling a threat actor to inject malicious queries and extract sensitive information, such as admin password hashes, granting elevated privileges. However, LDAP must be enabled on the Central Manager for this vulnerability to be exploitable.
CVE-2024-26026: Unauthenticated SQL Injection
This SQL injection vulnerability in the Next Central Manager could be present in any device configuration, possibly enabling a threat actor to bypass authentication and extract administrative user hashes from vulnerable devices. Apart from these two CVE-assigned vulnerabilities, there were three other unassigned vulnerabilities.
Undocumented API enables SSRF of URL path, allowing any device method to be called, potentially creating invisible onboard accounts. Additionally, the Central Manager hashes admin passwords with a low Bcrypt cost of 6, making them vulnerable to brute-force attacks, which could be executed with around $50k in resources.
Admin Password Self-Reset without Previous Password Knowledge – A logged-in Administrative user can reset their password without even knowing the previous password. If combined with the other vulnerabilities mentioned above, this could lead to escalated security risks.
Eclypsium has published a proof of concept for each vulnerability. Users are advised to upgrade their F5 assets to the latest versions to address these security issues.