CAPTCHAs, or Completely Automated Public Turing tests, are used online to verify users are human, not bots. They usually present challenges like distorted text, image recognition tasks, or audio prompts that require human cognitive skills.
All about fake “verify you’re human”
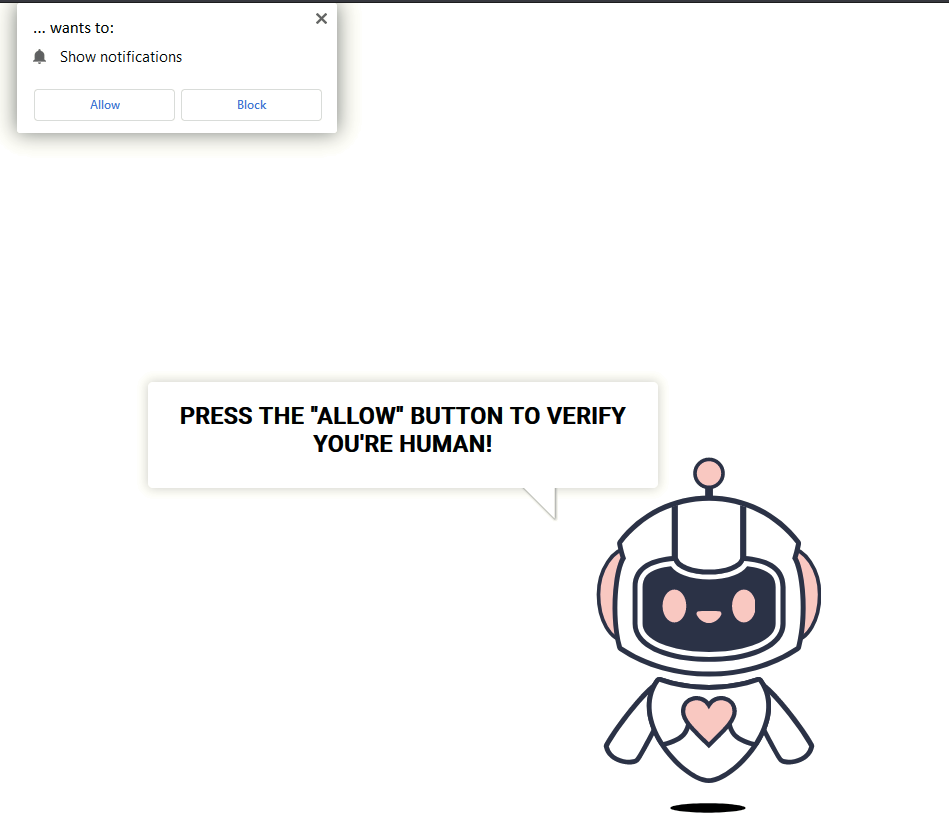
In September 2024, SecureWorks warned of fake “verify you are human” requests delivering malware. Their incident responders found two cases where users searching Google for sports and movie streaming sites were led to malicious websites.
They were both sent to a fake website that asked them to prove they were human by doing the following:
- Press “Windows + R” to open the Run menu
- Press “CTRL + V” to paste a hidden PowerShell command
- Press “Enter” to run it
This caused a ZIP file with malware to download, which was extracted to \AppData\Local\Temp\file\Setup.exe on the victim’s computer. The malware then ran more tools, including a renamed BitTorrent app (StrCmp.exe) and a Windows utility called Search Indexer.
SecureWorks CTU researchers found that this attack method deployed information-stealing malware, specifically Vidar and StealC, which harvest sensitive data from infected systems.
This cyber attack bypasses browser security by using a fake human verification prompt to open a command prompt on the victim’s computer. The attacker instructs the user to run unauthorized code and deploys malware like LummaC2 infostealer.
This global campaign has been reported in regions such as the Middle East, Australia, and France, with incidents occurring from May 2024 to September 2024.
Infostealer use has surged since 2023, with cybercriminals targeting various service credentials and company networks. Stolen accounts and passwords quickly sell on black markets like the ‘Russian Market.’
Recommendation
- Enhance Security Awareness Training: Educate employees on phishing and verification techniques.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require MFA for sensitive system access.
- Regularly Update Software: Keep all systems and antivirus programs current.
- Monitor Network Activity: Use security tools to detect unusual account behavior.
- Use Strong Password Policies: Enforce complex passwords and promote password managers.
- Limit Access to Sensitive Information: Apply least privilege principles for access control.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Assess security measures and response plans frequently.
- Employ Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Solutions: Detect and respond to threats in real time.
- Have an Incident Response Plan: Prepare to address data breaches effectively.
Follow Us on: Twitter, Instagram, Facebook to get the latest security news!












Leave A Comment