Apache RocketMQ, a widely used messaging system for handling high volumes of data and critical operations, often attracts hackers. Exploiting RocketMQ vulnerabilities allows attackers to disrupt communications, access sensitive information, and potentially control data flow.
Cybersecurity researchers at Aqua Nautilus recently discovered that Muhstik malware has been actively attacking the Apache RocketMQ platform to execute remote code.
Muhstik Malware
RocketMQ versions 5.1.0 and below had a remote code execution vulnerability (CVE-2023-33246), allowing attackers to execute commands by exploiting the insecure update configuration function.
Experts detected attacks exploiting this vulnerability to download Muhstik malware, part of the Kaiten family targeting Linux devices for cryptomining and DDoS attacks.
The attack flow begins by exploiting the RocketMQ flaw to upload and execute a malicious payload that fetches Muhstik, similar to previous Mirai-based attacks following that malware’s source code leak.
Researchers deployed a honeypot with a vulnerable RocketMQ version. Attackers detected and exploited the flaw to update the broker configuration, enabling remote code execution.
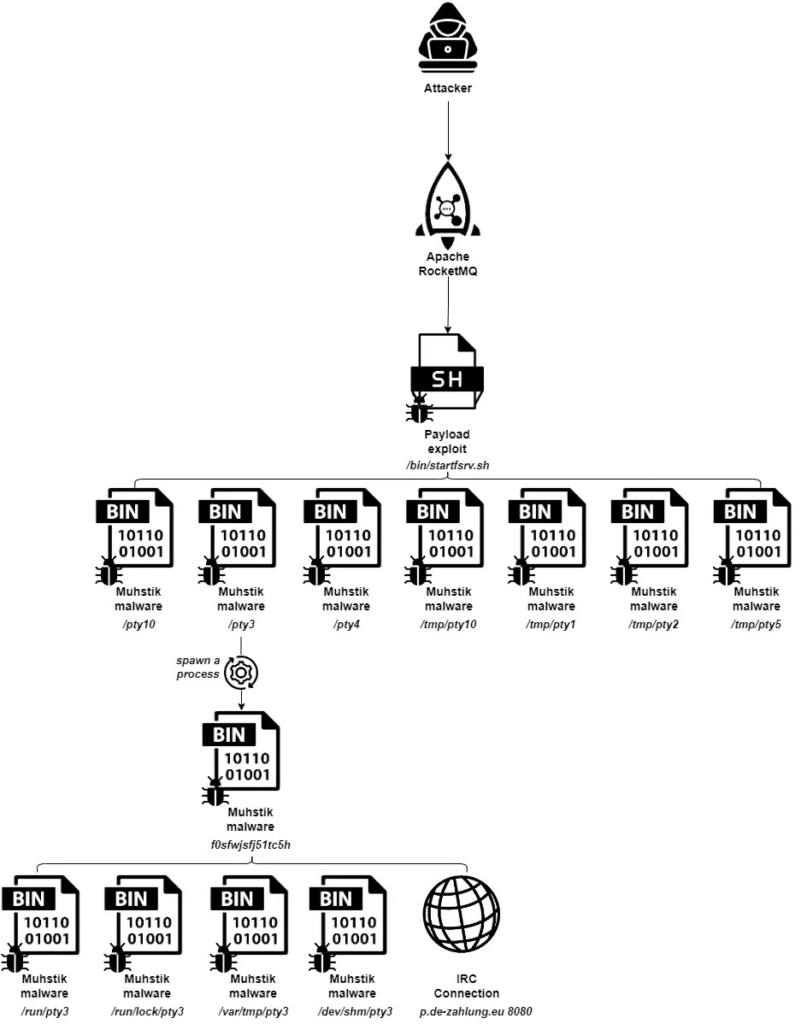
They delivered a malicious shell script that fetched Muhstik malware binaries matching the system architecture.
Muhstik then copied itself across directories like /dev/shm and edited inittab for persistence, ensuring it restarts on boot.
It employed fileless techniques, loading directly into memory from temporary locations to evade detection, and used a pty3 filename to masquerade as a legitimate process.
The Muhstik malware gathered system details via uname, checked for network monitoring tools like strace and tcpdump, scanned for SSH services, and communicated with a C2 server over IRC.
It connected to the identified malicious domain p.de-zahlung[.]eu, joining channel #ex86 with the password 8974.
An encrypted command instructed the cleanup of malicious processes like cnrig and kinsing using killall.
The malware persisted through PING and PONG exchanges, confirming an active IRC connection to receive further commands from the C2 server.
Muhstik monetizes compromised systems by removing other malicious processes, performing DDoS attacks, and cryptomining on infected computers.
The CVE-2023-33246 vulnerability left 5,200 RocketMQ instances globally exposed, according to Shodan scans by researchers. This underscores the risks of unpatched systems.
Security remains a top priority for companies with cloud-native applications, as new vulnerabilities and misconfigurations could expose their systems to attackers like Muhstik.
RocketMQ exemplifies messaging infrastructure that can aid developers in building more resilient applications.
Recommendations
Secure your environment: Ensure that all systems, networks, and applications are properly secured by implementing robust security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, and regular security updates. Additionally, enforce strong access controls, use encryption where necessary, and regularly audit and monitor your environment for any potential vulnerabilities or security gaps.
Scan your environment: Conduct regular security scans and assessments to identify and remediate any vulnerabilities or weaknesses in your systems and networks. Utilize both automated scanning tools and manual assessments to comprehensively evaluate your environment for potential security risks. Regular scanning helps to proactively detect and address security issues before they can be exploited by attackers.
Educate your employees: Provide comprehensive security awareness training to all employees to educate them about common security threats, best practices for securing data and systems, and how to recognize and respond to potential security incidents. Encourage employees to practice good security habits such as using strong passwords, being cautious of phishing emails, and reporting any suspicious activities promptly. Effective employee education and training are essential for building a strong security culture within your organization.













Leave A Comment