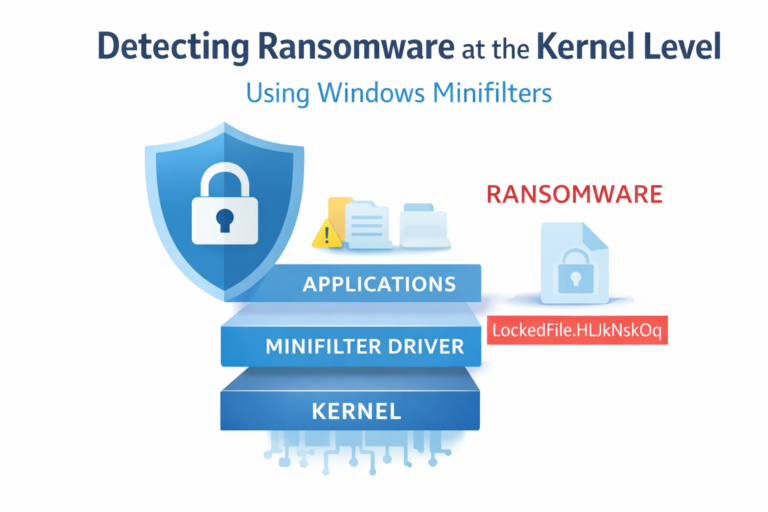
This time the ransomware relied more on compromising exposed RDP connections to gain an initial foothold on a target network.
Ransom.Ryuk
Ransom.Ryuk is used in targeted attacks, where the threat actors make sure that essential files are encrypted so they can ask for large ransom amounts, observed since late 2018.
This means the attackers first find a way into the networks and use tools to map them out.
Attack Technique
Initial infection vector for the threat actor using targeted phishing emails to deliver the malware.
Furthermore, the actors have a new preference when it comes to gaining initial access to the victim network.
To gain initial access to a network most often through two methods in 2021.
- Service-Based RDP Compromise
- Botnet-Based Malware Delivery
According to Security researchers from the threat intelligence boutique Advanced Intelligence (AdvIntel) observed that Ryuk ransomware:
- Firstly, the actors have been running “large-scale brute force and password spraying attacks against exposed RDP hosts” to compromise user credentials
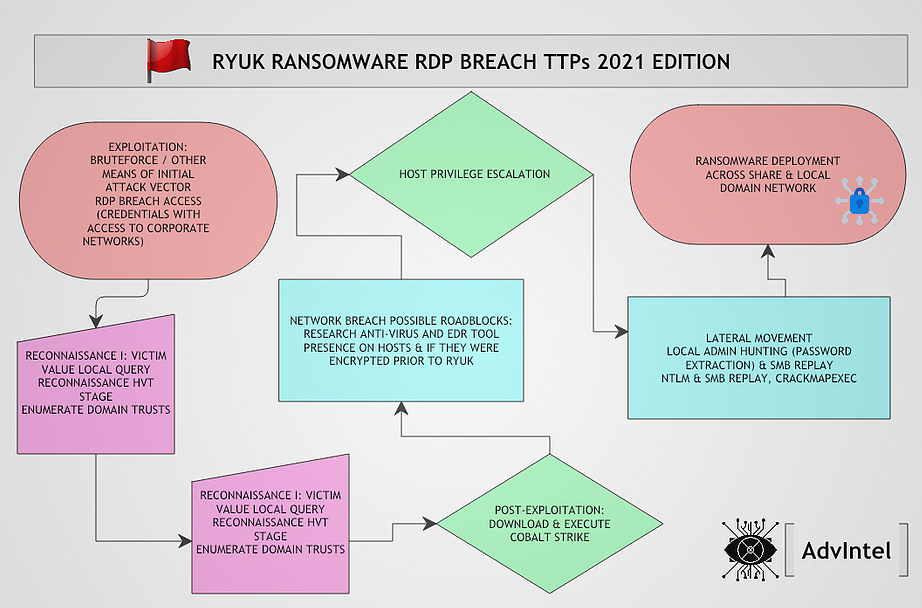
- Reconnaissance I: Victim Value Local Reconnaissance Stage – the actors attempt to gather information about the organization to determine what resources within the infected domain are of value to perpetrating the rest of the attack.
- Reconnaissance II: ZoomInfo and Open Source Target Revenue Enrichment – specifically, actors have been observed searching across services such as ZoomInfo to retrieve information about the victim company such as
- technologies used
- recent mergers and acquisitions
- corporate hierarchies
- personnel, and various other elements of data related to the company that may be of value to their operations.
- Post-Exploitation: Cobalt Strike as Golden Standard Tool – After infection, Ryuk operators utilize Post-Exploitation toolkits such as Cobalt Strike to conduct further reconnaissance and operation.
- Network Breach Possible Roadblocks: Anti-Virus & Endpoint Detection Response Bypass – actors will utilize information collected by bot scans and their own scans to gain information about anti-virus (AV) and Endpoint Detection Response (EDR) tools present on hosts before formulating their attack.
Once the operators successfully compromise a domain administrator account, they will work to disable AV and EDR services.
Novel Red Team Technique
- Hunting for a local IT administrator with access to EDR software and leveraging a PowerShell tool “KeeThief.ps1” to extract administrator credentials for EDR software from popular KeePass password manager
- Allows for the extraction of KeePass 2.X key material from memory, as well as the backdooring and enumeration of the KeePass trigger system.
- Deploying portable Notepad++ version to run PowerShell scripts on the host system to bypass PowerShell executionrestriction. The portable Notepad++ includes PowerShell version 1.
According to AdvIntel, Ryuk ransomware attacks this year are exploiting two vulnerabilities to increase their permissions on a compromised machine. Both flaws are older and patches are available for them:
- CVE-2018-8453 is an elevation of privilege vulnerability in Windows 7 through 10 and Windows Server 2008 through 2016 when the win23k.sys component fails to properly handle objects in memory. The exploitation of this vulnerability allows an attacker to run an arbitrary kernel with read/write privileges.
- CVE-2019-1069 – an elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the way the Task Scheduler Service validates certain file operations, aka ‘Task Scheduler Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability’
Security Mitigation
Once actors have successfully compromised a local or domain admin account, they distribute the Ryuk payload through Group Policy Objects, PsExec sessions from a domain controller, or by utilizing a startup item in the SYSVOL share.
However, below are the security steps recommended for an organization:
- Detections for use of Mimikatz and PsExec execution within the network.
- Detections and alerts for the presence of AdFind, Bloodhound, and LaZagne within the network.
- Ensure all operating systems and software are up to date with the latest updates and security patches.
- Implement multi-factor authentication for RDP access.
- Implement network segmentation and controls to scrutinize SMB and NTLM traffic within the network.
- Routinely review account permissions to prevent privilege creep and maintain principle of least privilege.
- Routinely review Group Policy Objects and logon scripts.
- Also, Update systems to prevent exploitation of CVE-2018-8453 and CVE-2019-1069.