An innovative SMTP Smuggling technique has been reported with the capability to circumvent current security protocols. Additionally, it empowers attackers to send forged emails that appear to originate from authentic addresses. This could inject renewed vitality into email spam, as its effectiveness has not waned over the recent period.
WHAT IS SMTP SMUGGLING?
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) Smuggling is a technique used by attackers to manipulate the behavior of mail servers during the email transmission process. It involves exploiting inconsistencies or variations in the way different servers interpret and implement the SMTP protocol.
In a typical SMTP transaction, there are two phases: the client’s request to the server (DATA phase) and the server’s response. SMTP Smuggling takes advantage of discrepancies in how proxy servers and mail servers interpret the length of the message content during these phases.
By carefully crafting the headers and body of an email, attackers can deceive the servers into misinterpreting the message length, leading to discrepancies between the front-end proxy server and the back-end mail server. This can result in various security issues, such as bypassing security filters, evading detection, and enabling malicious activities like spoofing or injecting arbitrary content into emails.
SMTP Smuggling attacks are a type of protocol-level manipulation, exploiting the intricacies of communication between different components in the email delivery process. Defending against SMTP Smuggling often involves implementing secure and consistent configurations across all involved mail servers and proxies to prevent the exploitation of these protocol variations.
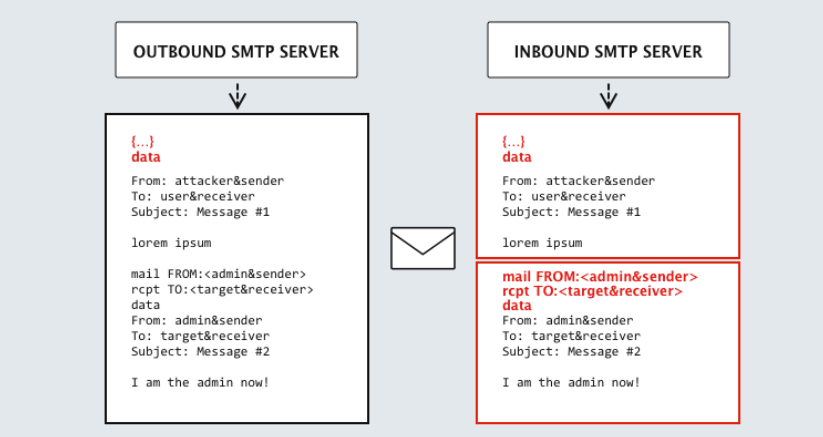
SMTP smuggling centers around inconsistencies in how distinct servers process the end-of-data sequence (<CR><LF>.<CR><LF>). Through exploiting these variations, attackers can escape the standard message data, introducing unauthorized commands.
This method relies on the inbound server’s ability to accept multiple SMTP commands in a batch, a functionality widely supported by most servers today.
Thorough investigation into this vulnerability has uncovered that SMTP servers belonging to major email providers such as Microsoft, GMX, and Cisco are susceptible to this exploit. Although Microsoft and GMX have taken steps to address these issues, Cisco has categorized the findings as a feature rather than a vulnerability and has opted not to modify the default configuration.
WHAT IS THE DANGER OF SMTP VULNERABILITY?
SMTP smuggling poses alarming implications as attackers can send deceptive emails from seemingly credible sources, evading authentication checks like DKIM, DMARC, and SPF.
In essence, employing this technique could allow fraudsters to infiltrate corporate emails previously immune to spam. While companies implementing this security method are likely cognizant of the risks and employ additional protective measures, the exposure itself increases the overall vulnerability to potential cyberattacks.
MITIGATING THE EFFECTS OF VULNERABILITY
To mitigate the effects of SMTP vulnerability:
- Implement Security Updates: Regularly update and patch SMTP servers to address known vulnerabilities and ensure they are equipped with the latest security measures.
- Enable Encryption: Utilize encryption mechanisms, such as STARTTLS, to secure the communication channels between SMTP servers and prevent eavesdropping or unauthorized access.
- Protocol Compliance: Ensure that SMTP servers adhere to standardized protocols and follow best practices to minimize the risk of exploitation through protocol-level vulnerabilities.
- Network Monitoring: Implement robust network monitoring tools to detect unusual SMTP traffic patterns, which may indicate potential exploitation or malicious activities.
- Authentication Mechanisms: Strengthen authentication mechanisms, including enforcing strong passwords and implementing multi-factor authentication, to prevent unauthorized access to SMTP servers.
- Implement Access Controls: Configure access controls to restrict access to SMTP servers only to authorized personnel, reducing the risk of unauthorized manipulation or exploitation.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential weaknesses in the SMTP infrastructure.
- User Awareness Training: Educate users about phishing attacks and social engineering tactics that may exploit SMTP vulnerabilities, emphasizing vigilance in email interactions.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Deploy intrusion detection and prevention systems to monitor and block suspicious activities or unauthorized access attempts targeting SMTP servers.
- Collaborate with Vendors: Stay informed about vendor advisories, security updates, and patches related to SMTP vulnerabilities, and promptly apply recommended mitigations.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and maintain an incident response plan specific to SMTP vulnerabilities, outlining procedures for detecting, responding to, and recovering from potential security incidents.
- Backup and Recovery: Regularly back up critical email data and ensure the availability of efficient recovery mechanisms to minimize data loss in the event of a security breach.
Follow Us on: Twitter, Instagram, Facebook to get the latest security news!













Leave A Comment