Kinsta, a leading WordPress hosting provider, has alerted its customers to a troubling cybersecurity development.
Cybercriminals are exploiting Google Search Ads to promote phishing websites, with a focus on pilfering user credentials—especially those associated with Kinsta’s crucial service, MyKinsta, used for managing WordPress and other cloud-based applications.
KINSTA PHISHING: HACKERS EXPLOIT GOOGLE ADS
In an email notification, Kinsta reveals that cybercriminals are employing Google Ads as their primary method for phishing attacks.
These malicious actors intentionally focus on individuals who have previously visited Kinsta’s official websites. They create deceptive websites closely resembling Kinsta’s own, skillfully luring users to click on them.
The email from Kinsta states:
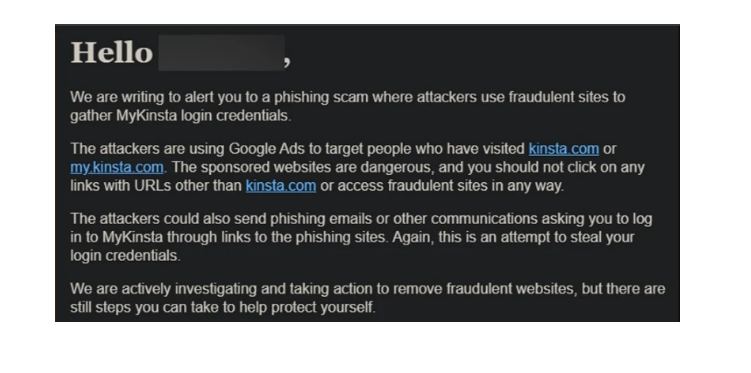
The main goal was to entice users to input their Kinsta login credentials on the fraudulent website. Once obtained, attackers could leverage these credentials to access users’ WordPress websites, potentially leading to severe consequences. This may involve:
- Compromised websites may expose sensitive information, including customer data, financial details, and intellectual property.
- Attackers could inject malicious code into compromised websites, redirecting visitors to phishing sites or facilitating the spread of malware. The website’s content may be defaced or substituted with malicious messages.
- Access to payment gateways or sensitive financial information could result in financial losses for users or their clients.
- A successful phishing attack might tarnish Kinsta’s reputation, raising concerns about its security measures and eroding user trust.
Google Ads, a widely-used advertising platform, is regrettably gaining popularity among hackers and cybercriminals, who exploit its broad reach and visibility for various malicious activities.
Google Ads were used to promote counterfeit downloads for popular software such as Grammarly, MSI Afterburner, Slack, Dashlane, Malwarebytes, Audacity, μTorrent, OBS, Ring, AnyDesk, Libre Office, Teamviewer, Thunderbird, and Brave on several websites.
PROTECTING AGAINST PHISHING THREATS
To safeguard against phishing threats:
- Stay Informed: Stay updated on the latest phishing tactics and techniques.
- Verify Emails: Verify the legitimacy of emails, especially those requesting sensitive information or containing unexpected links.
- Use Security Software: Employ reliable antivirus and anti-phishing tools to detect and prevent phishing attempts.
- Check URLs: Hover over links to preview the destination URL before clicking. Be cautious of misspellings or slight variations in web addresses.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Add an extra layer of security by enabling 2FA on your accounts.
- Educate Users: Provide training and awareness programs to educate individuals about recognizing and avoiding phishing attempts.
- Report Suspicious Emails: Encourage users to report any suspicious emails promptly.
- Regularly Update Software: Keep software, browsers, and security tools up to date to patch vulnerabilities.
- Use Secure Connections: Ensure that websites use HTTPS, and avoid entering sensitive information on unsecured sites.
- Implement Email Filtering: Utilize advanced email filtering systems to identify and block phishing emails before they reach users.
- Employ DMARC Protection: Implement DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) to prevent email spoofing.
- Conduct Simulated Phishing Tests: Regularly conduct simulated phishing tests to evaluate users’ susceptibility and reinforce security awareness.













Leave A Comment